IMAGINE A GRAND PRIX ON A FORMULA 1 TRACK THAT IS 110 MILLION KILOMETRES LONG, WITH 150,000 PITS FOR THE TEAMS AND TENS OF MILLIONS OF PIT STOPS SO THAT RACE PERFORMANCE CAN BE ORGANISED IN THE BEST POSSIBLE WAY. JUST THINK ABOUT 30,000 TECHNICIANS AND AN INVESTMENT OF 12 BILLION EUROS BETWEEN 2016 AND 2018, OF WHICH 4.5 BILLION EUROS ARE ALLOCATED TO ULTRA BROADBAND! We are actually referring to our network, the one that allows us to call, check our e-mails, update the social networks or watch a video online.
We are talking about the Telecom Italia telecommunication network, which, thanks to Open Access has opened up, providing access services to other operators, as well as the essential technical support for other operators. Telecommunications and their “circuit” are so much a part of us that they are no longer a service, but a natural solution. As a matter of fact, they are all the infrastructures and equipment that allow individuals and/or devices to communicate by exchanging data, images or sounds.
ONE NETWORK LEADS TO ANOTHER
Initially, every network had to manage just one service but in the course of the years, due to obvious communication needs and to the technological development, networks began to overlap and stratify.
Today, single-service networks use and share common infrastructures (optical fibre, copper cables, radio bridges, etc.) known as a Transmission Network, which supports, for instance, two services that are essential to us: the telephone network and the broadband Internet access network.
The closer we get to the centre of the network, all traffic types (voice and data) are changed into formats that the IP Router can manage.
THE TRANSFORMATION PROCESS IS NECESSARY BECAUSE NOT ALL TRAFFIC TYPOLOGIES ARE COMPATIBLE WITH THAT OF THE ROUTERS.

The traditional Voice Telephone Network works by following a routing logic called Circuit Switch Logic. The communication between two callers is ensured by a specific transmission channel that enables a continuous and constant flow of communication.
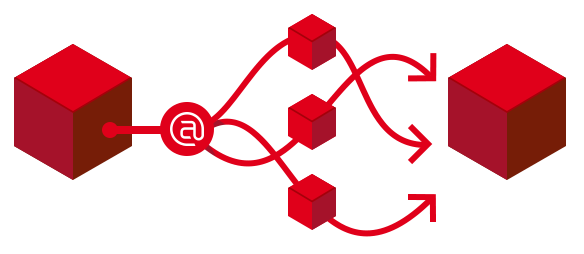
IP networks work thanks to the packet switching, which divides data flow into many small “packets” that reach their destination by different routes and occupy transmission networks only when necessary, thus ensuring a much more efficient and faster service.
THE BROADBAND NETWORK
The Broadband is a type of connection that we are all familiar with, we have at least heard of it or perhaps we know it under a different name, essentially we use it to surf the Internet at high speed.
In most cases, this type of connection is implemented, in our homes or in our offices, via the copper cables of the traditional telephone network.
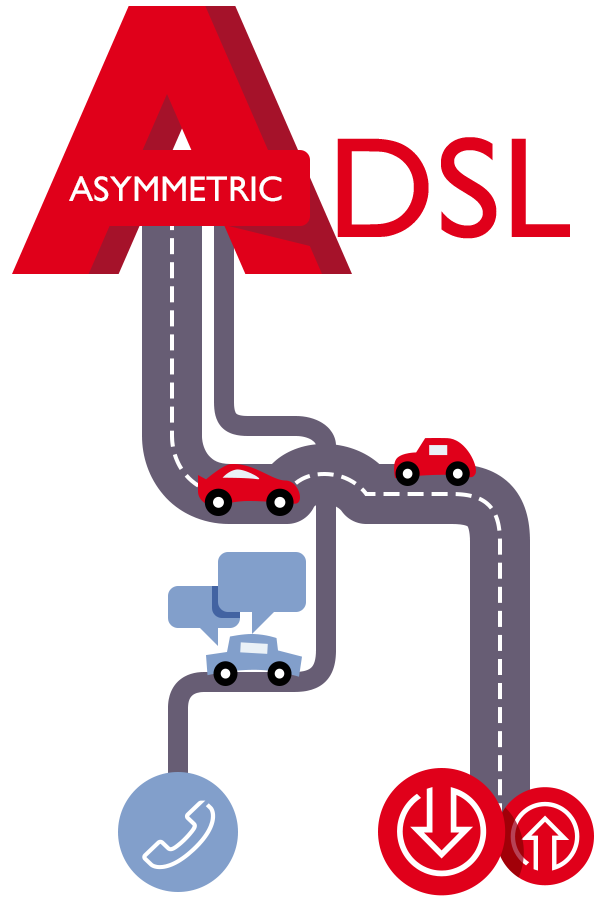
To make the traditional telephone network accessible via broadband, we use the technologies of the xDSL (Digital Subscriber Line) family, whereof the most popular and widespread is ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line).
This is the acronymwe know best but do we really know, for instance, what the “A” in ADSL stands for?
The “A” stands for “Asymmetric” and defines the main feature of this technology, which is like a two-way mountain road where the traffic to the user (downstream) goes at a speed much higher than that of the traffic going in the opposite direction (upstream).
However, this happens without affecting the voice traffic service that can continue to use the portion of transmission spectrum that it needs.
THE NETWORK CARRIES VOICE TRAFFIC (ANALOG) AND DATA TRAFFIC (DIGITAL) AT THE SAME TIME
HOW DOES THE COMPANY DO IT?
DSLAM
it collects users’ lines at the telephone exchange, connecting them to the Telecom Italia geographical network and then to the Internet network.
THE MODEM
it turns the digital information of computers into electrical signals that can travel along traditional analog networks.
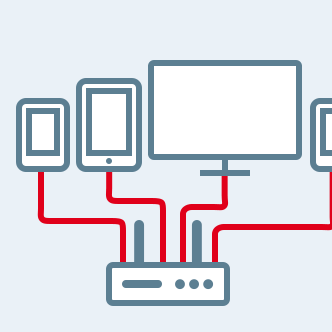
THE ROUTER
it connects several devices to the broadband network and has the task of routing and managing traffic on a local network.
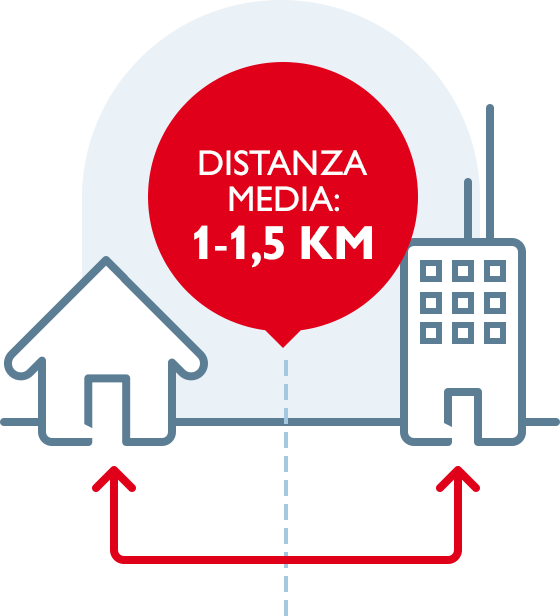
ADSL PERFORMANCE GREATLY DEPENDS ON THE LENGTH OF THE DISTRIBUTION NETWORK.
The further away the user’s home is from the telephone exchange, the lower the maximum speed that can be reached.
For historical reasons, in Italy we have built a “short” distribution network, namely, a network with telephone exchanges located at an average distance of 1 – 1.5 km from buildings: obviously, this ensures higher efficiency than that of other countries.
ADSL IS JUST THE MOST POPULAR OF THE BROADBAND NETWORKS
In fact, we also have ADSL2 and the ADSL2+ that can reach speeds of up to approximately 12 and 24 Mbit/s downstream and 1 Mbit/s upstream.
NGAN: THE EVOLUTION OF OPTICAL FIBRE
An alternative way to connect to broadband is by Optical Fibre connections.
TELECOM ITALIA HAS UPGRADED THE OPTICAL FIBRE NETWORK, CREATING NGAN, THE NEXT GENERATION ACCESS NETWORK, A POINT OF EXCELLENCE OF OUR COMPANY.
This network allows us to download and send data faster, ensuring a higher download and upload speed to landline connections, also providing the opportunity to connect from different devices at the same time without affecting the quality of the connection.
THE GROUP IS INVESTING IN ORDER TO SPREAD THE OPTICAL FIBRE NETWORK TO ALL TOWNS AND CITIES. BY OCTOBER 2016 NGN COVERAGE REACHED 56% OF THE HOUSES.
This is also the aim of the “TIM Italia Connessa” contest, which awards investments in stationary and mobile NGN infrastructures to municipalities with the most innovative digital development projects.
INVESTING IN OPTICAL FIBRE
For a telco company, this means intervening on the entire structure, replacing existing cables with new optical fibre cables. We decided to make this costly commitment in order to bring ultra Internet into every home
THE MOBILE RADIO COMMUNICATION NETWORK
Do you remember TACS? It was the standard used by mobile phones in the early 1990s, however, in 1995, the GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication) standard began to spread overwhelmingly. It was the first European digital standard known as the second generation standard (or 2G).
Today, the transition to third generation mobile phones (3G) with the UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System) standard is in full development, while the race to a fourth generation (4G) mobile telephone network with LTE (Long Term Evolution) has already started.

THE ACCESS NETWORK
Namely, mobile phones and radio base stations
THE CORE NETWORK
It includes the nodes that collect and distribute calls (MSC Mobile Switching Center or MGW Mobile Gateway) and perform normal management functions. The core network also manages functions such as mobility and safety. Its basic elements are, not by chance, the databases that contain customer-targeted information such as their ID the services they have subscribed to, customizations and invoice-related data.

THE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
it is the OMC (Operations and Maintenance Center) that monitors and controls all aspects to ensure that they are in operation and manage any needed maintenance work.
4G LTE: THE LONG-TERM EVOLUTION
THE MOST ADVANCED UPDATE OF THE UMTS NETWORK IS THE LTE (LONG TERM EVOLUTION) NETWORK
This ensures much higher efficiency than the already advanced HSPA (High Speed Packet Access) network, designed to improve the efficiency of 3G networks.
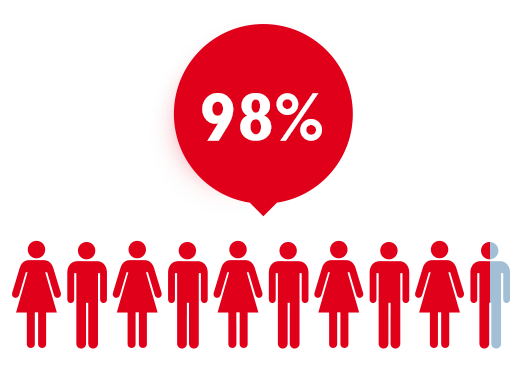
The 4G LTE network made its appearance in 2012 in the main Italian cities such as Rome, Naples, Turin and Milan, obtaining great success from the start and recording a higher than expected growth rate in the mobile ultrabroadband offer. By October 2016 LTE coverage reached 95% of population.
THE GROUP'S GOAL
is to reach 98% coverage of the Italian population by the end of 2017.
THE NETWORK OF CONTENTS
Traffic growth (also thanks to the latest generation networks) has made it necessary to introduce a service that can guarantee maximum quality of content, which is now largely accessed directly via the Internet.
Online gaming, HD video and audio streaming are now available not only thanks to systems such as optical fibre and LTE but also to the CDN (Content Delivery Network) system, which is being increasingly used.
THE CDN IS A STRUCTURE THAT ALLOWS DATA AND MULTIMEDIA CONTENT TO “APPROACH” USERS, THANKS TO PRE-UPLOAD ON CACHE MEMORIES DISTRIBUTED ON THE NETWORK AND THEREFORE CLOSER TO USERS.
Therefore, several users connecting to the same content access it via different physical locations, leading to a clear improvement in the quality of the service provided.
The current CDN of Telecom Italia is distributed on 19 PoPs (Points Of Presence) of the OPB (Optical Packet Backbone) network allowing efficiency levels to be reached that are definitely higher than other transport infrastructures.
TELECOM ITALIA IS LOOKING INTO THE FEASIBILITY OF CREATING A SINGLE CDN, A SHARED INFRASTRUCTURE TO MEET THE REQUIREMENTS OF EVERY COMPANY IN OUR GROUP AND DISTRIBUTED THROUGHOUT THE THREE COUNTRIES WHERE WE OPERATE: ITALY, BRASIL AND ARGENTINA.
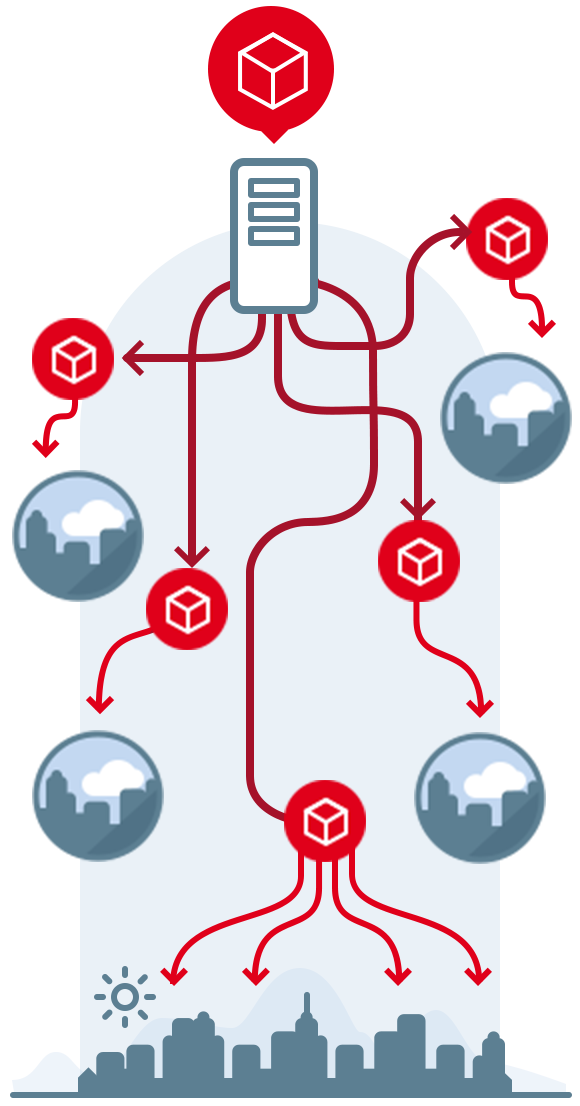
THE NETWORK OF DATA AND THINGS
Having talked about networks and technologies, we also need to add the many services that each of us uses every day by providing our data: bank services, mail services, insurance services, etc. But what makes all this possible? Data Centers.
TELECOM ITALIA USES 8 DATA CENTERS DISTRIBUTED THROUGHOUT THE NATIONAL TERRITORY, WHOSE BASIC FUNCTIONS ARE TO PROVIDE STORAGE AND SERVICES, ACHIEVING THE OPTIMIZATION OF ENERGY CONSUMPTION.
Taking into account the high efficiency achieved and corresponding energy consumption (equivalent to that of a small town), systems have evolved to achieve a drastic reduction in energy consumption of up to 25%, thanks to top European solutions such as Eco4Cloud.
about 37,000
M2
about 20,000
SERVERS
about 500
PROFESSIONALS
![]()
THE NETWORK IS ALSO THE NETWORK OF THINGS, REAL ONES, THAT ARE PART OF OUR LIFE: IT IS CALLED THE “INTERNET OF THINGS”.
It is a network of many sensors, capable of registring data and connecting them in order to configure a physical object (for example an alarm clock) on the basis of a particular event (for example traffic).
How does the sensorial network work? In the event of high traffic amounts, the alarm clock will receive the input to ring earlier so as to allow us to get to work in time, avoiding long traffic jams, and bringing a real and tangible advantage to our everyday life.
IN HEALTHCARE
To monitor the patients’ physiological data, to manage the hospital or identify allergies.
ENVIRONMENTAL APPLICATIONS
Fire detection; control of river levels or air pollution levels.
COMMERCIAL APPLICATIONS
Anti-theft, car-tracking, controlling public utilities such as the office heating system.
ENERGY APPLICATIONS
Energy consumption monitoring
HOME APPLICATIONS